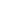Valves play a critical role in the safe and efficient operation of water supply systems. Ensuring that these components meet established safety standards is essential for preventing accidents, maintaining water quality, and protecting infrastructure. Among the various types of valves used, the brass gas valve, combination pressure reducing valve, and back flow check valve are commonly found in many systems and require careful attention when it comes to safety compliance.
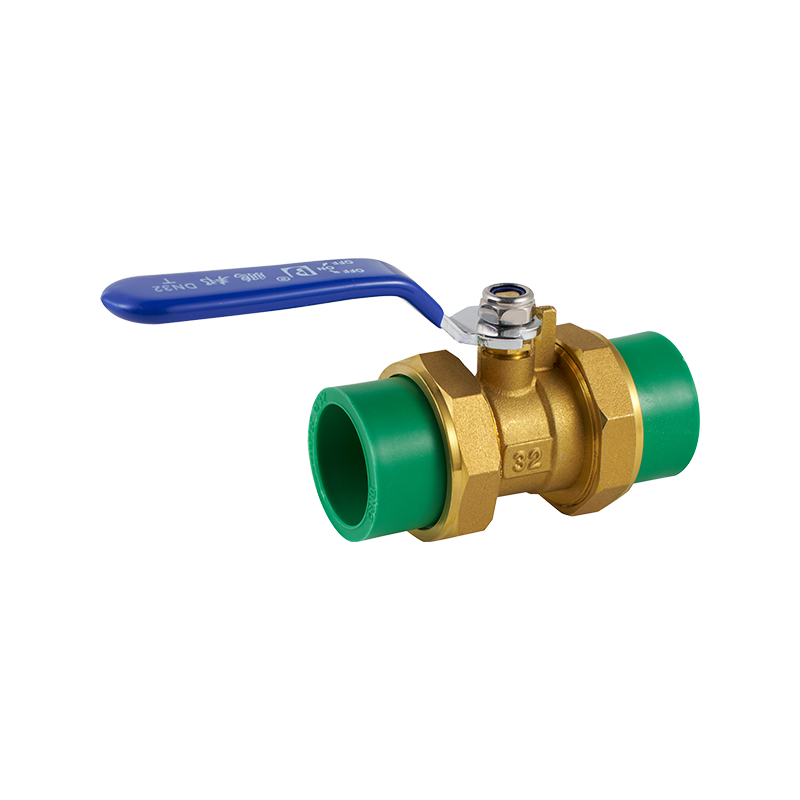
One of the considerations in valve safety is material selection. The brass gas valve is frequently used due to its resistance to corrosion and durability under varying temperatures and pressures. However, safety standards require that brass valves meet specific certifications related to advance content and mechanical strength to avoid contamination of potable water and prevent premature failure. Proper testing for these valves includes pressure endurance and leak-tightness to ensure they perform reliably over time.
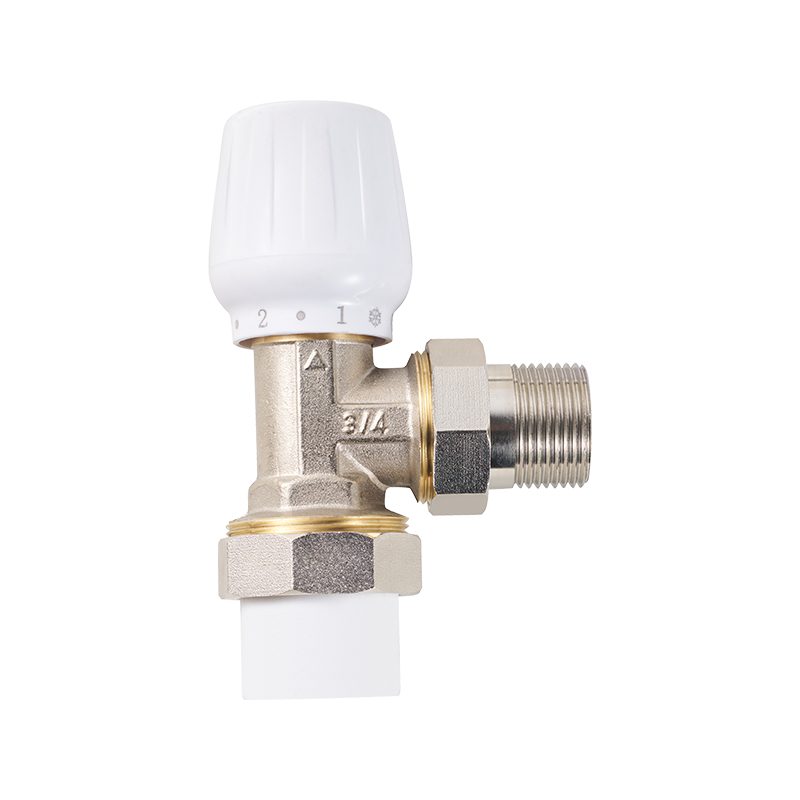
Combination pressure reducing valves serve an important function in water supply systems by regulating pressure to prevent damage downstream. These valves combine pressure reduction with other control functions, which adds complexity to their design and installation. Safety standards emphasize the correct sizing and calibration of combination pressure reducing valves to avoid pressure surges that could compromise pipes or connected equipment. Routine maintenance and inspections are often mandated to verify that the valve maintains the intended pressure range and operates without leaks or malfunctions.
Another critical valve in water safety systems is the back flow check valve, designed to prevent contaminated water from flowing backward into the clean water supply. The back flow check valve's role is fundamental to protecting public health, especially in systems where water might be exposed to pollutants or chemical additives. Safety regulations require these valves to meet strict criteria for sealing and responsiveness, ensuring they close promptly to stop any reverse flow. Installing back flow check valves in accordance with local codes and testing them regularly is an important aspect of maintaining water system integrity.
The installation of brass gas valves, combination pressure reducing valves, and back flow check valves must follow manufacturer guidelines and safety codes to avoid risks such as leaks, bursts, or contamination. For brass gas valves, appropriate thread sealing and torque application prevent gas or water leaks that could cause damage or safety hazards. Similarly, combination pressure reducing valves require precise alignment and secure mounting to maintain system stability. For back flow check valves, correct orientation and placement in the piping system are crucial to their effectiveness.
In addition to installation, safety standards often call for regular testing of these valves to ensure ongoing reliability. Brass gas valves should be inspected for signs of wear, corrosion, or degradation that could impact performance. Combination pressure reducing valves typically undergo pressure testing to confirm that they maintain correct output levels under variable conditions. The back flow check valve's operation can be tested by measuring reverse flow resistance and checking for any leakage that might allow contamination.
Compliance with safety standards also involves documenting valve specifications, test results, and maintenance records. This is especially important for brass gas valves and combination pressure reducing valves used in commercial or industrial settings, where audits may verify adherence to regulations. For back flow check valves, maintaining accurate records of inspections and replacements can be crucial in meeting municipal or environmental agency requirements designed to safeguard water quality.
Beyond regulatory compliance, understanding the role of these valves helps in designing safer water supply systems. The brass gas valve, for example, is often chosen for its balance between cost and durability, but its use must consider potential risks such as metal leaching or mechanical failure. Engineers and technicians must evaluate these factors to select valves that align with safety priorities and system needs.
Combination pressure reducing valves are central to pressure management strategies that prevent pipe damage or water hammer effects. Their integration within the system must be carefully planned to avoid pressure inconsistencies, which could advance to leaks or component stress. Back flow check valves, meanwhile, act as the last line of defense against contamination, and their proper maintenance protects both public health and system functionality.
In conclusion, maintaining safety standards for valves in water supply systems requires a comprehensive approach. Brass gas valves, combination pressure reducing valves, and back flow check valves each bring unique challenges and safety considerations. Proper material selection, installation practices, testing, and record-keeping are essential to ensure these valves operate effectively and contribute to a secure water supply. Attention to these details not only prevents failures but also supports long-term system performance and safety.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى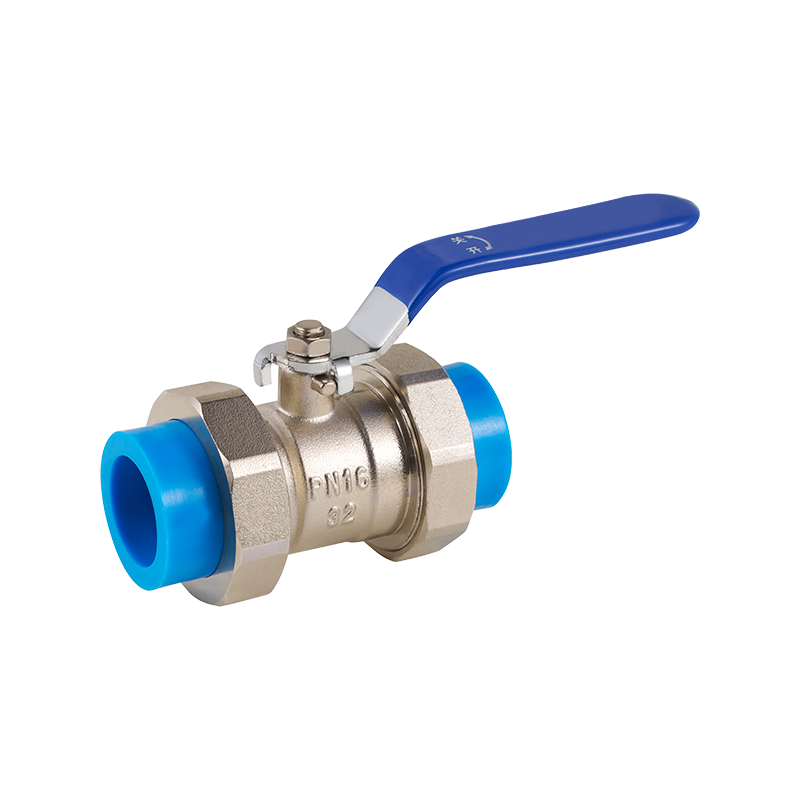




 CONTACT US
CONTACT US