Testing and quality control in valve manufacturing are critical steps that ensure products meet the necessary safety and performance standards. In industries where valves such as the house gas valve, high temperature pressure reducing valve, and inline air check valve are essential components, thorough testing is not just a formality but a requirement that safeguards both equipment and users.

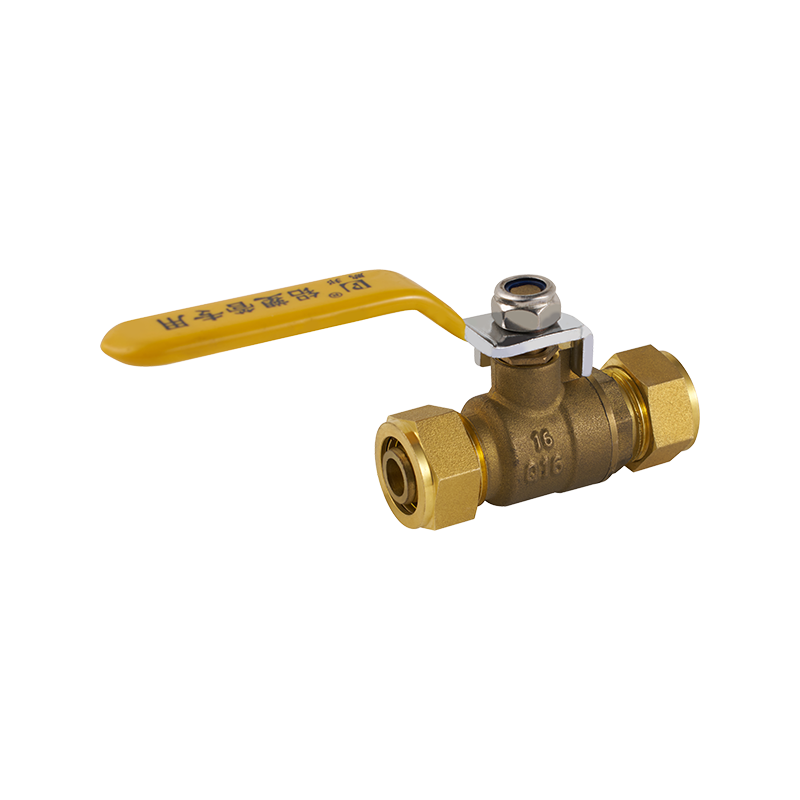
When manufacturing a house gas valve, precision and reliability are especially important. This type of valve plays a vital role in controlling the flow of gas within residential or commercial heating systems. A failure in a house gas valve could advance to dangerous leaks or inefficient system operation. For this reason, manufacturers put significant effort into testing these valves to confirm their durability under various pressure and temperature conditions. The valve must consistently regulate gas flow without allowing leaks or pressure drops that could compromise safety or functionality.
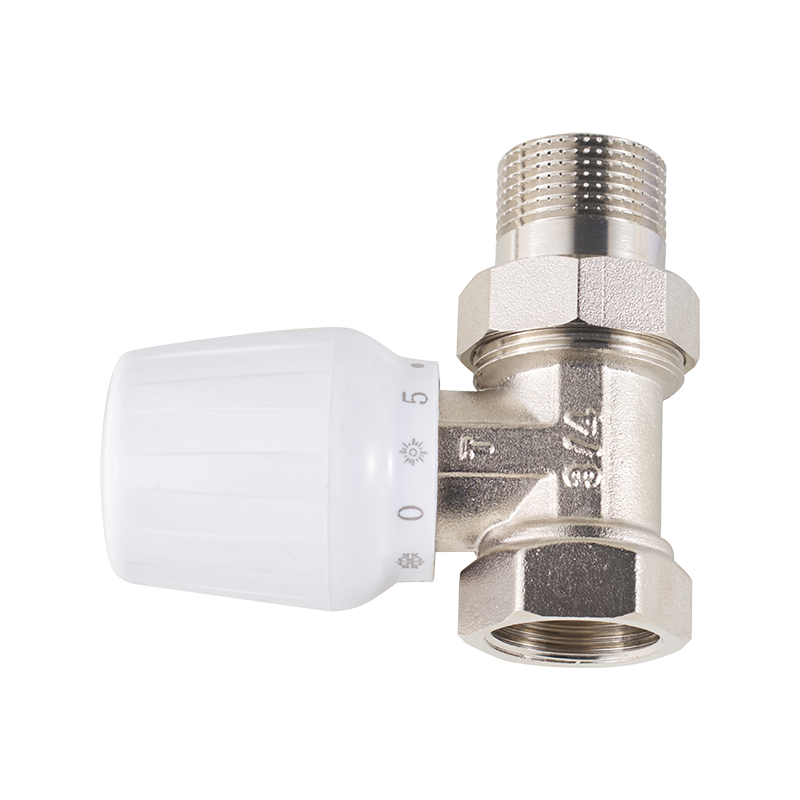
The high temperature pressure reducing valve presents a different set of challenges during quality control. This valve is designed to manage pressure in systems that operate under elevated temperatures. In industrial settings, such valves often regulate steam or hot water flows. Testing for this valve type usually involves subjecting it to cycles of bad heat and pressure to assess its ability to maintain consistent output pressure and prevent overpressure scenarios. The valve's material quality, sealing effectiveness, and mechanical integrity all come under scrutiny. Because the high temperature pressure reducing valve operates in harsh environments, testing procedures often simulate real-world conditions to ensure reliability over time.
Similarly, the inline air check valve serves a crucial function in preventing backflow in pneumatic systems or compressed air lines. Unlike valves that regulate pressure or flow, the inline air check valve is designed to allow air to pass in only one direction. Testing this valve involves verifying its sealing performance under different flow rates and pressures to ensure no reverse flow occurs. A faulty inline air check valve could result in system contamination or damage due to backflow. Manufacturers carry out leak tests, cycle tests, and endurance tests to confirm the valve's capability to function without failure over extended periods.
Throughout the production process, valve manufacturers rely on several types of testing methods. For a house gas valve, leak testing is among the more critical. By applying pressurized gas or air and monitoring for any leaks, manufacturers can quickly identify faults in seals or welds. This test is repeated multiple times, often using different pressures to mimic operating conditions, ensuring the house gas valve remains reliable under all expected scenarios.
The high temperature pressure reducing valve undergoes performance testing where the valve is installed in a test rig that simulates system pressure and temperature. Sensors monitor the valve's ability to reduce and maintain pressure within a set range. Any deviations from target pressure or signs of instability can indicate design or manufacturing flaws. Additionally, materials are tested for heat resistance and corrosion to ensure the valve will perform as intended throughout its service life.
Testing an inline air check valve usually includes flow direction tests and endurance tests. During the flow direction test, air is pushed through the valve in the intended direction to ensure small resistance and proper opening. Then, air is applied in the opposite direction to confirm the valve closes completely and prevents any backflow. Repeating these tests over many cycles helps ensure the valve's components won't wear prematurely.
Quality control in valve manufacturing is not limited to product testing alone. It also involves strict oversight of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and assembly techniques. For valves like the house gas valve, components must be sourced with consistent quality to prevent weak points. The high temperature pressure reducing valve requires precision machining and high-grade materials to withstand demanding conditions. The inline air check valve depends on careful assembly and correct component tolerances to ensure tight sealing and smooth operation.
Manufacturers implement standards and certifications as part of their quality assurance programs, which often include routine audits and documentation. These measures help maintain consistency across production batches and support traceability in case of product recalls or warranty issues. For valves used in critical applications, this layer of quality control adds confidence that each house gas valve, high temperature pressure reducing valve, and inline air check valve meets the performance expectations.
In conclusion, testing and quality control in valve manufacturing are vital to producing components that operate safely and reliably. Whether dealing with a house gas valve, a high temperature pressure reducing valve, or an inline air check valve, thorough testing under simulated conditions helps identify weaknesses early. Combined with material inspection and process controls, these practices ensure that valves fulfill their roles in controlling flow, pressure, and direction effectively in various systems. The commitment to detailed testing ultimately protects users and maintains system efficiency over time.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






 CONTACT US
CONTACT US