One significant impact of national standards is the uniformity they bring to valve types and performance criteria. Take, for example, the automatic check valve. This valve is designed to allow fluid flow in one direction while preventing backflow, which could damage equipment or contaminate water supplies. National standards specify the pressure ratings, material compatibility, leakage limits, and functional testing requirements for these valves. Such standards ensure that any automatic check valve produced under their scope will perform reliably in the intended applications, whether in residential plumbing or industrial piping systems.
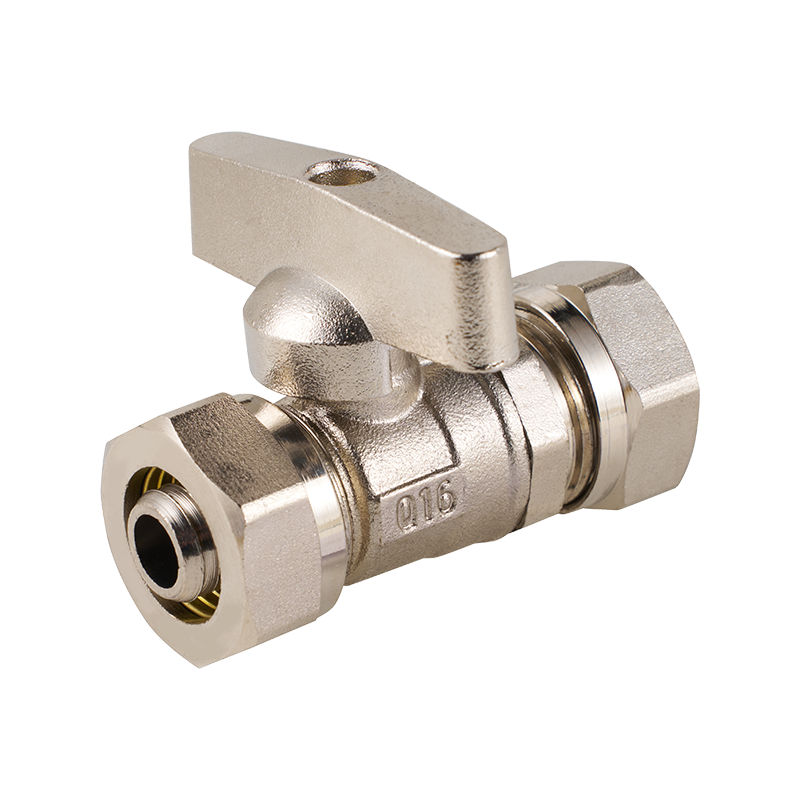

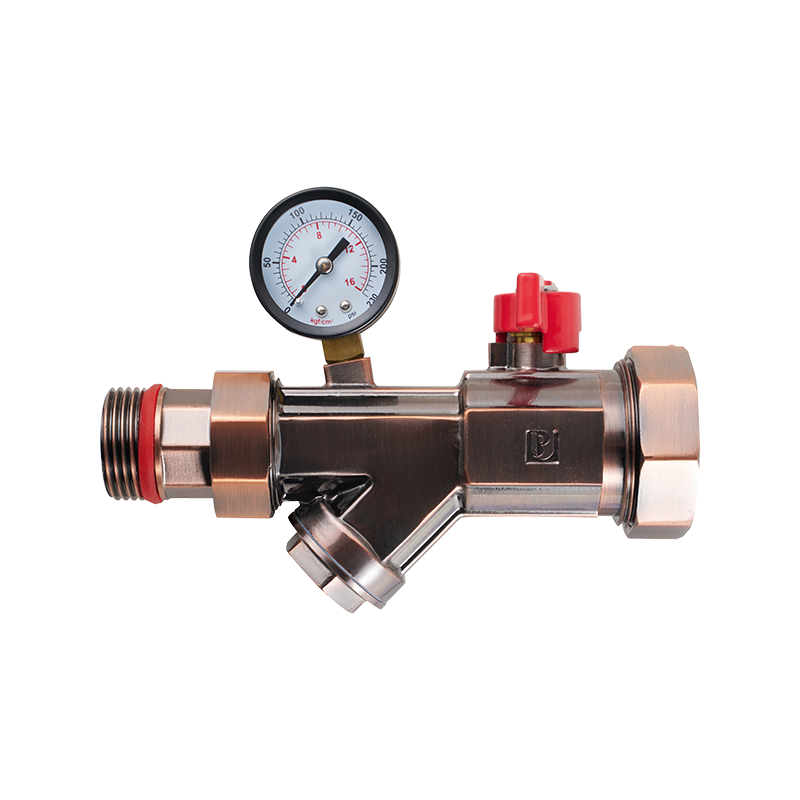
Similarly, the automatic pressure reducing valve is another component greatly influenced by standardized design principles. This valve is responsible for maintaining a consistent downstream pressure despite fluctuations in upstream supply, which protects downstream equipment and improves system stability. National standards define the acceptable pressure reduction ranges, response times, and durability requirements for these valves. These criteria guide designers in choosing appropriate materials and internal mechanisms, balancing responsiveness with longevity. Without clear standards, valve manufacturers might produce widely varying designs, pilot to unpredictable performance and safety concerns.
Manual valves are no less affected by national regulations. The manual gas shut off valve, a critical safety device in many gas supply systems, must meet stringent standards to ensure quick and reliable operation during emergencies. Standards cover factors such as operational torque, leak tightness, temperature resistance, and marking for identification. These requirements shape the valve's construction, including handle design, sealing materials, and connection types. By following national standards, manufacturers help ensure that users can operate these valves safely and efficiently when needed.
Beyond individual valve specifications, national standards influence the overall approach to pipe design as well. They specify dimensions, wall thicknesses, and pressure ratings for different pipe materials such as steel, copper, or polypropylene. This harmonization allows pipes and fittings to be interchangeable and compatible across different manufacturers and systems. It also facilitates inspections and certifications, as pipes meeting national standards are easier to evaluate for compliance and expected performance.
Moreover, the standards mandate rigorous testing protocols to verify that pipes and valves meet the necessary requirements before entering the market. Tests for mechanical strength, pressure endurance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability are common. This testing helps identify potential design flaws and material weaknesses early in production. For instance, pressure testing a valve assembly ensures that it will withstand operating pressures without leaking or failing. Such protocols reinforce confidence in the safety and longevity of plumbing and heating systems.
Another important aspect is the environmental and health considerations incorporated into national standards. Materials used for pipes and valves must not release harmful substances into water or air. Standards often restrict the use of certain hazardous compounds and encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly materials and processes. This push has led to broader acceptance of plastic piping systems such as PP-R pipes, which combine durability with safer chemical profiles. It also affects valve material choices, where corrosion-resistant metals or approved polymers are preferred to maintain system integrity without health risks.
Designers also benefit from standardized terminology and labeling requirements included in national standards. Clear labeling of valve types, pressure ratings, flow directions, and connection sizes helps installers and maintenance personnel identify the correct components quickly and avoid installation errors. This consistency across products reduces the likelihood of mistakes that could cause leaks or system failures. In emergency situations, such as operating a manual gas shut off valve, clear markings can be critical to user safety.
In conclusion, national standards are more than just regulatory hurdles; they form the foundation for consistent, safe, and functional pipe and valve designs. From automatic check valves that prevent backflow, to automatic pressure reducing valves that maintain stable pressures, and manual gas shut off valves that provide essential emergency control, every component is shaped by detailed standards. These guidelines foster compatibility, reliability, and safety across the plumbing and heating industries. As technology advances and new materials emerge, national standards will continue to evolve, ensuring that designs meet both current and future needs without compromising on safety or performance.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى





 CONTACT US
CONTACT US