In recent years, the plumbing and heating industry has witnessed steady improvements in valve design, driven by the rising demand for energy efficiency and system reliability. From residential buildings to industrial facilities, the role of valves in controlling the flow of water, gas, and heat is fundamental. A new generation of valves is now being developed not just for basic functionality but to contribute actively to the reduction of energy waste and system downtime.
One major shift in valve design focuses on the internal flow path geometry. Engineers have started to optimize valve interiors to reduce turbulence and pressure loss, which are critical factors affecting energy consumption in water and heating systems. By allowing a smoother flow, these redesigned valves reduce the workload on pumps and water heaters. Over time, this translates into measurable energy savings, especially in systems that operate continuously.
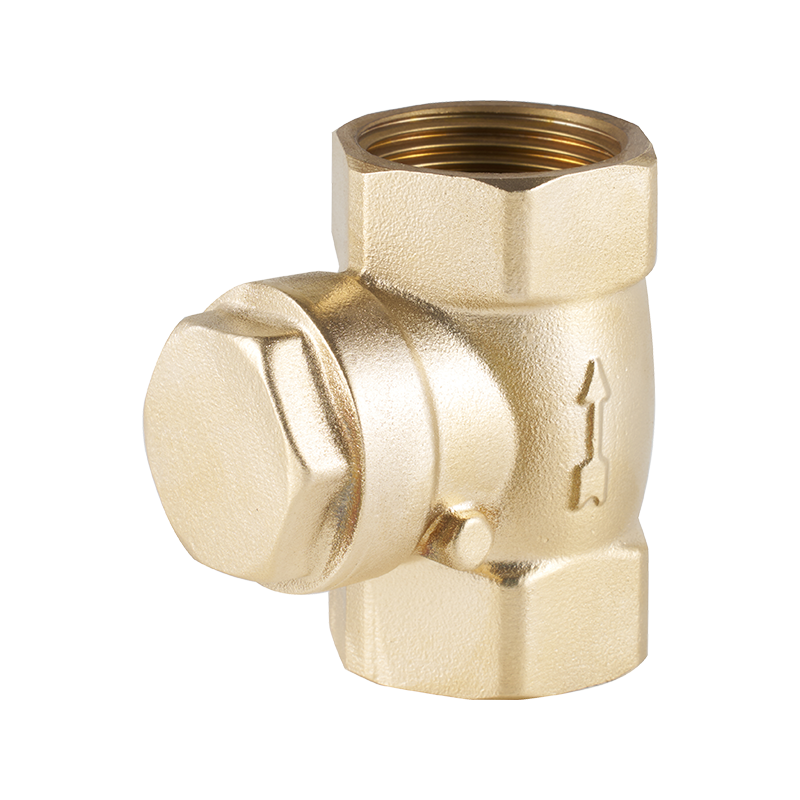

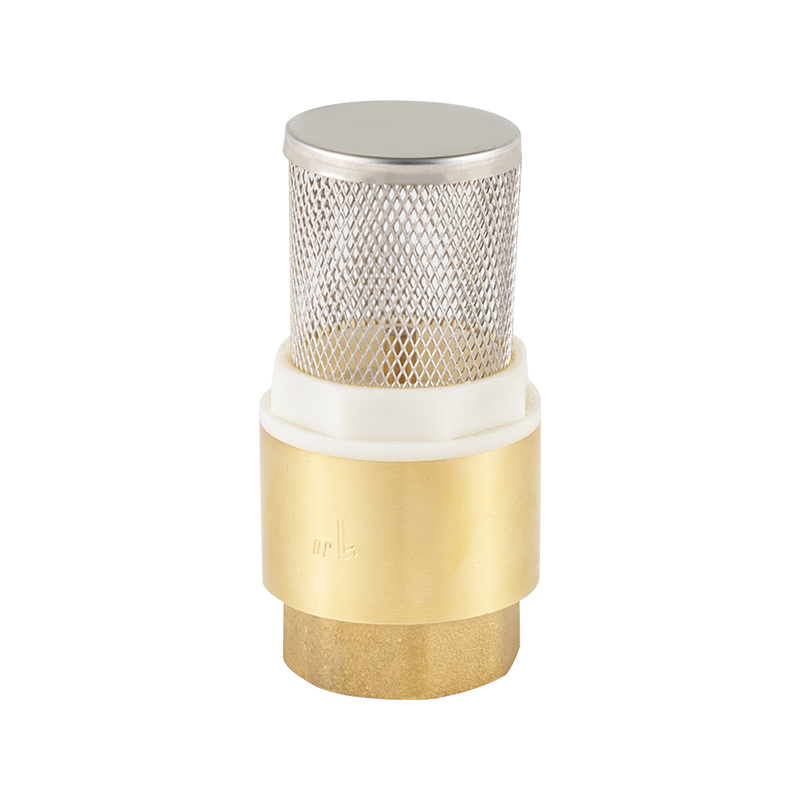
A clear example of this evolution can be seen in the copper pipe ball valve, a staple component in both residential and commercial plumbing systems. Traditionally valued for its durability and resistance to corrosion, the copper pipe ball valve is now being refined with low-friction seals and compact handles. These features enhance the flow-through efficiency while making installation more convenient, especially in tight spaces. Some newer models are even designed with integrated flow limiters, which help reduce unnecessary water usage without compromising performance.
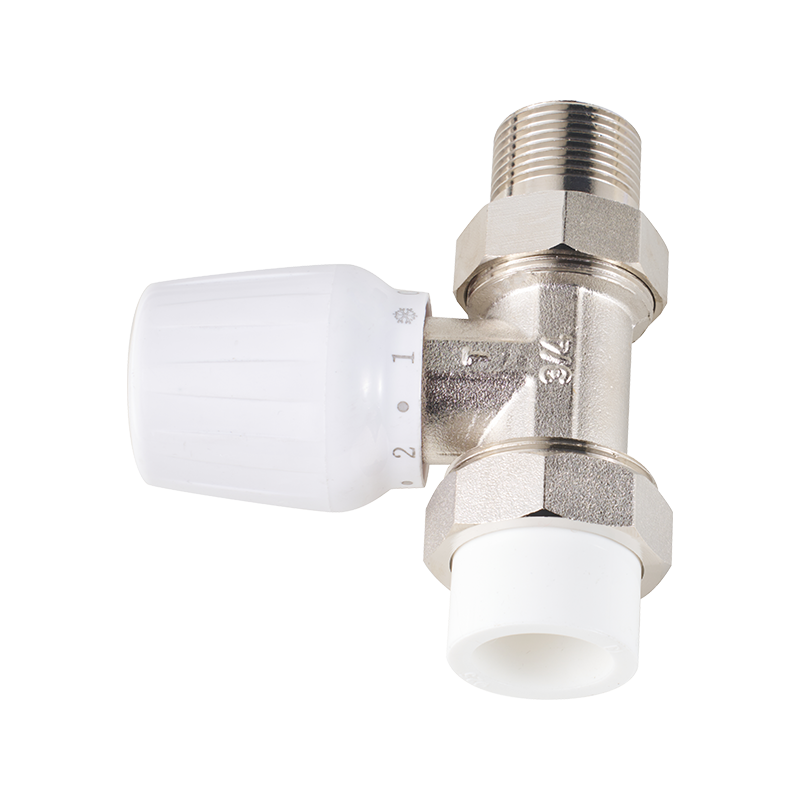
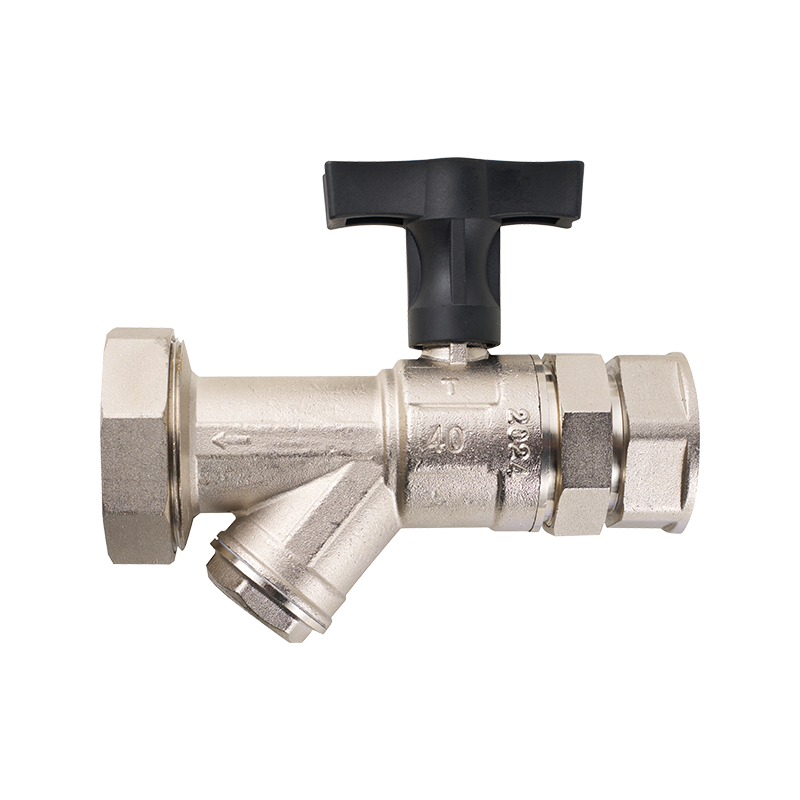
Another noteworthy advancement is the integration of safety features into energy-efficient valve systems. The safety lock valve, for instance, has been increasingly adopted in both domestic and industrial applications. Its function goes beyond simply controlling flow; it provides a secure mechanism to prevent accidental or unauthorized operation. This is particularly useful in gas and hot water systems where incorrect valve manipulation could advance to system inefficiencies or safety hazards. The inclusion of safety locks ensures that valves remain in the intended position, reducing the risk of leaks or flow disruptions that can compromise energy performance.
Materials and construction techniques are also undergoing thoughtful upgrades. For instance, precision machining combined with better polymer and metal alloys is being used to create tighter seals and reduce internal wear. These improvements advance to a longer valve service life and consistent flow control, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement—a factor that also contributes to sustainability and cost efficiency over the product's lifecycle.
Smart valve integration is another area where innovation meets energy efficiency. Many new systems now include automated control valves that can be adjusted remotely or programmed based on usage patterns. Although such smart technology may not yet be universal, it's gradually finding its way into larger buildings and commercial heating applications. These valves can react to changes in pressure, temperature, and flow demand, allowing systems to operate only when needed, thereby saving energy.
In everyday applications, basic components like the water tap ball valve are also seeing upgrades. Once considered a simple on-off device, today's water tap ball valve may feature ergonomic handles, precision ball mechanisms, and water-saving aerators. These upgrades not only improve user comfort but also reduce water wastage at the source. In homes where hundreds of liters of water pass through taps daily, the savings add up quickly—both in terms of energy used to heat the water and the water itself.
The future of valve technology lies in continuous refinement—making small but impactful changes that improve both energy performance and usability. As plumbing and HVAC systems grow more complex, the importance of each component increases. Innovations in valve design—such as smoother flow paths, improved sealing materials, integrated safety features, and automation readiness—are all part of a broader effort to support energy conservation.
For manufacturers and installers alike, paying attention to these evolving features is essential. Choosing a valve is no longer just about flow control; it's about contributing to the overall energy strategy of a system. Whether it's a copper pipe ball valve tucked behind a wall, a safety lock valve securing a heating line, or a water tap ball valve at the kitchen sink, every component plays a role in shaping a more efficient and responsible plumbing future.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى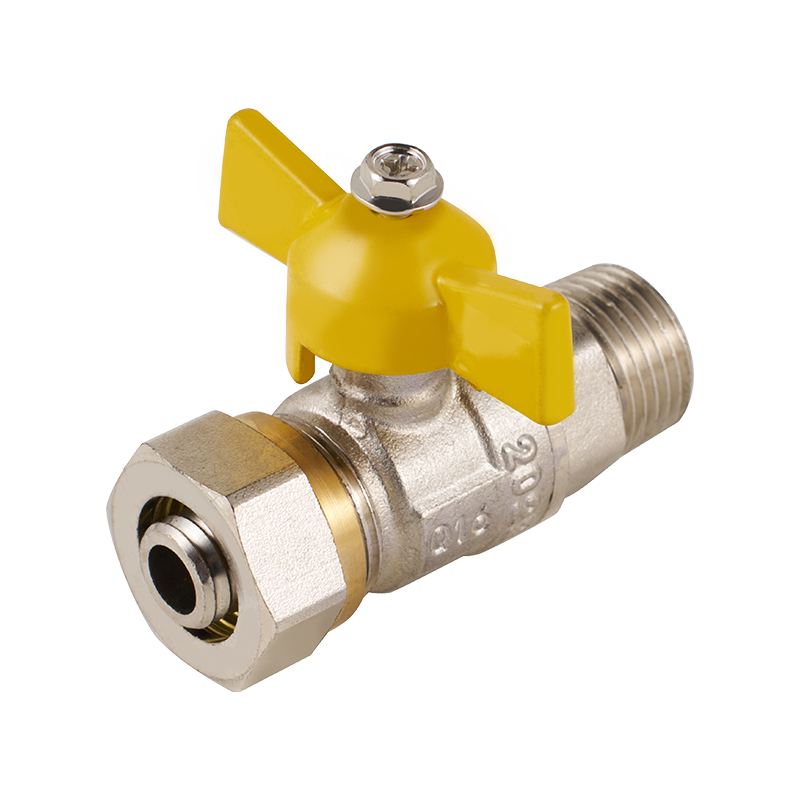






 CONTACT US
CONTACT US