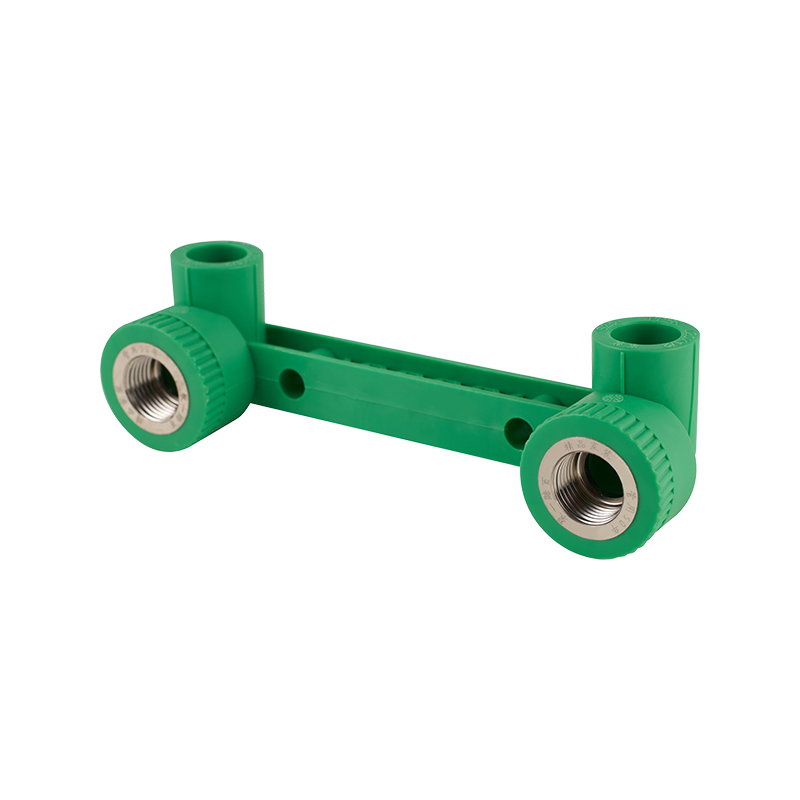
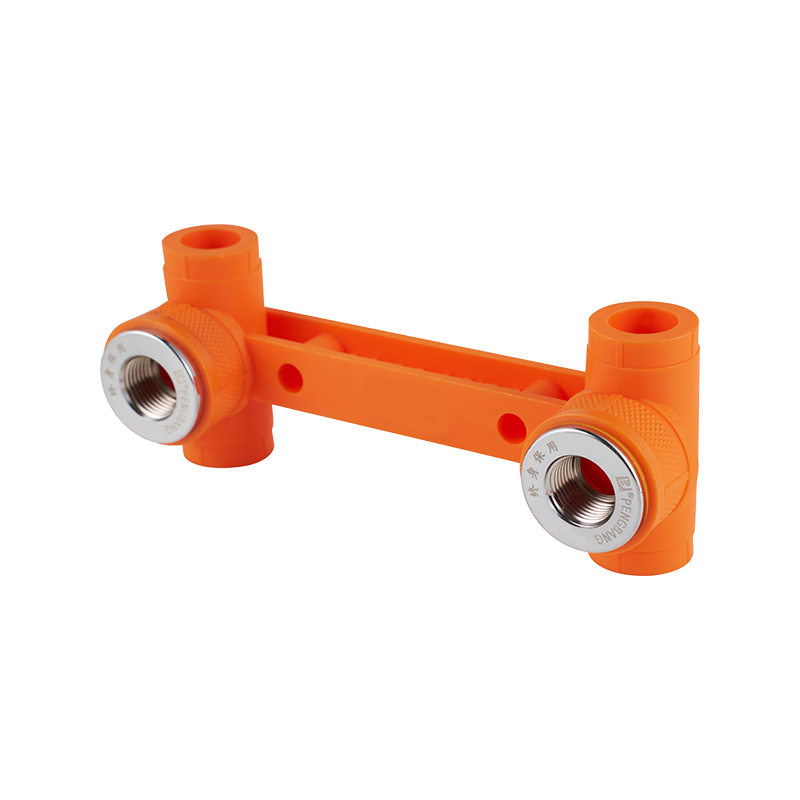
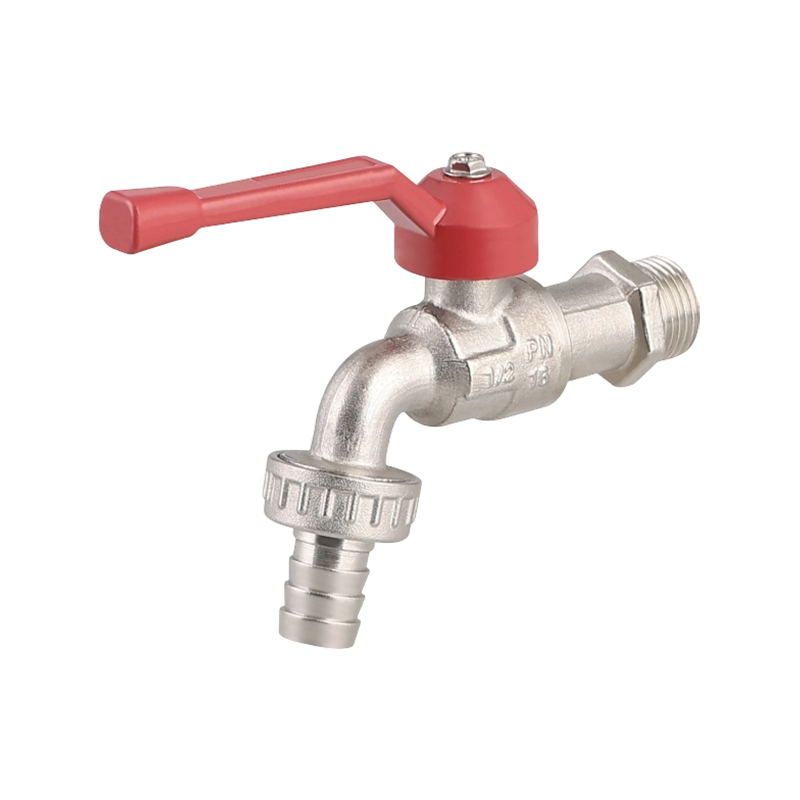
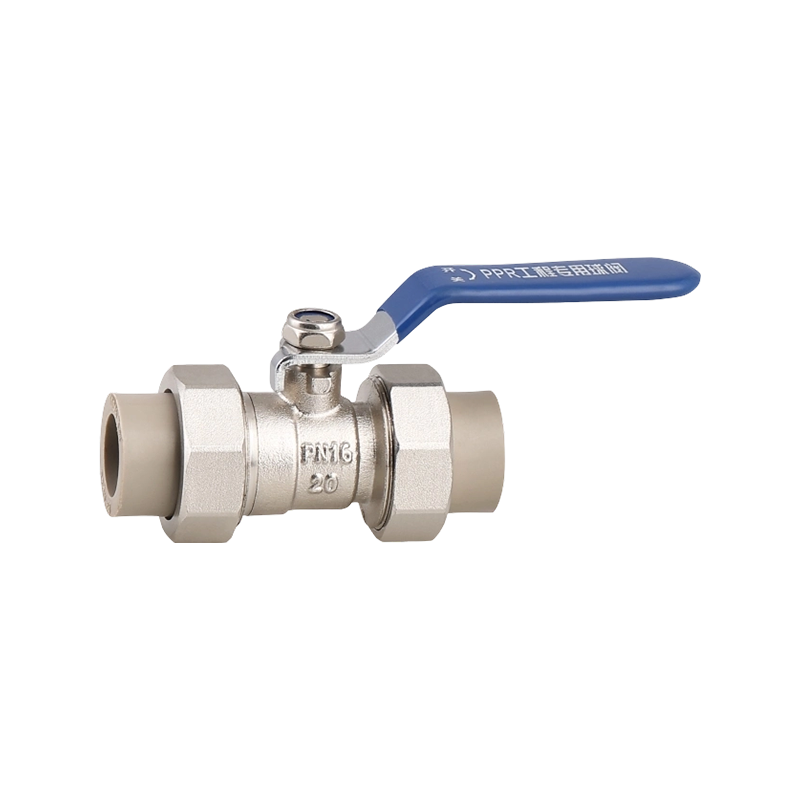
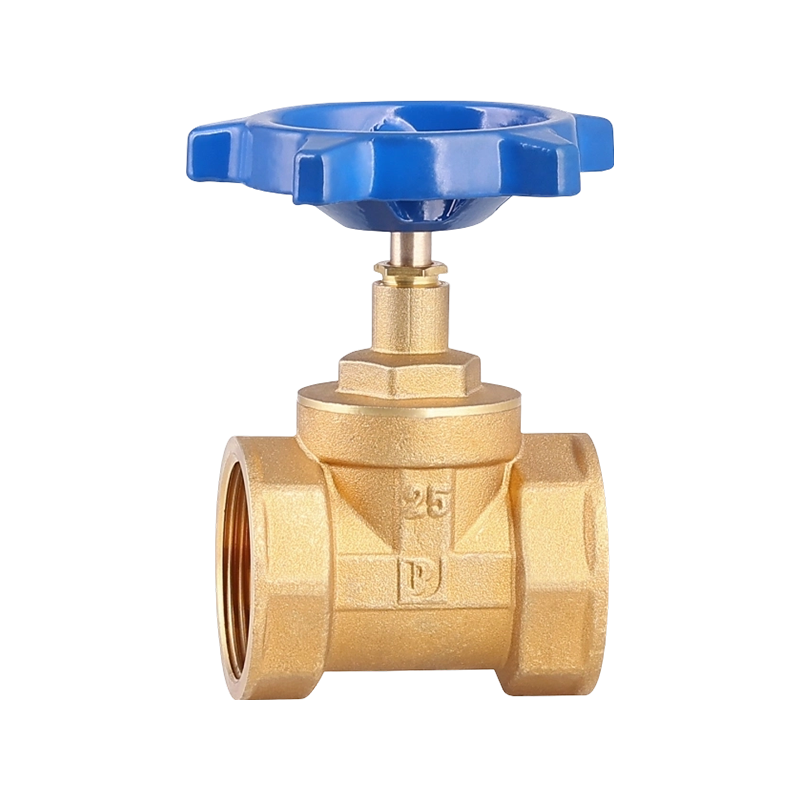
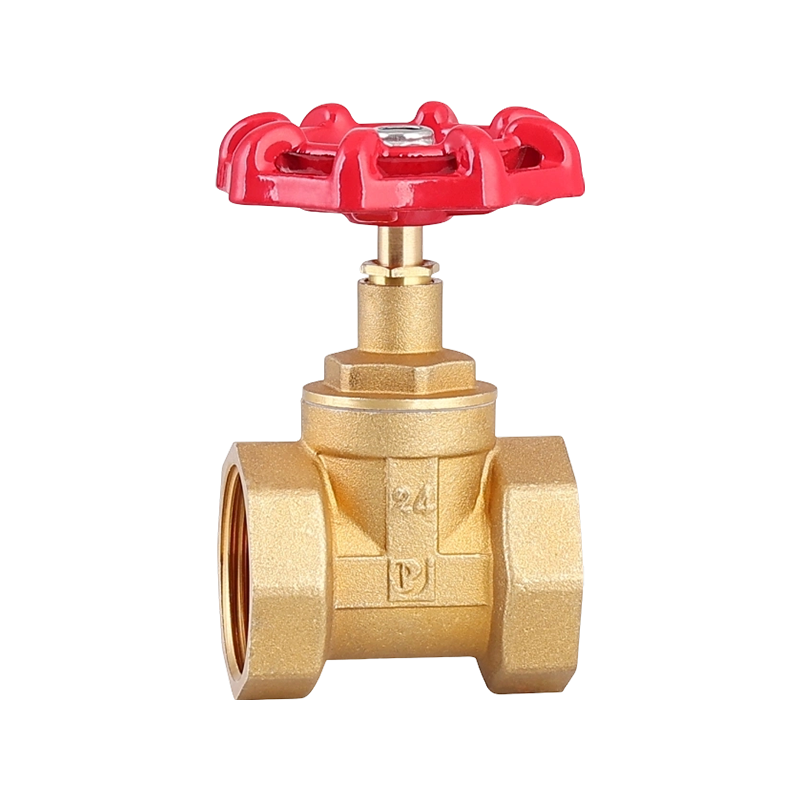
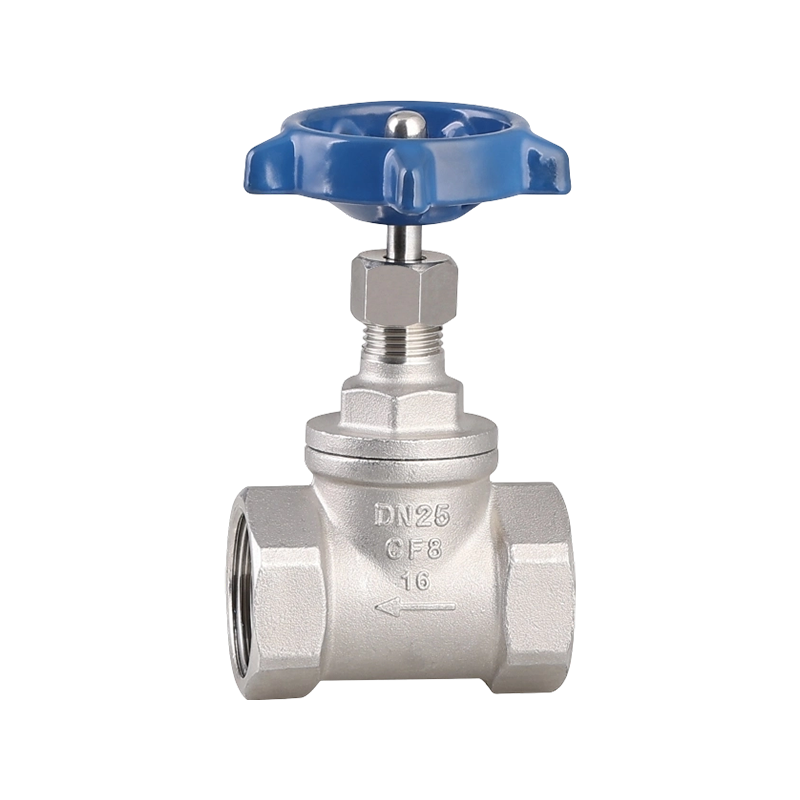
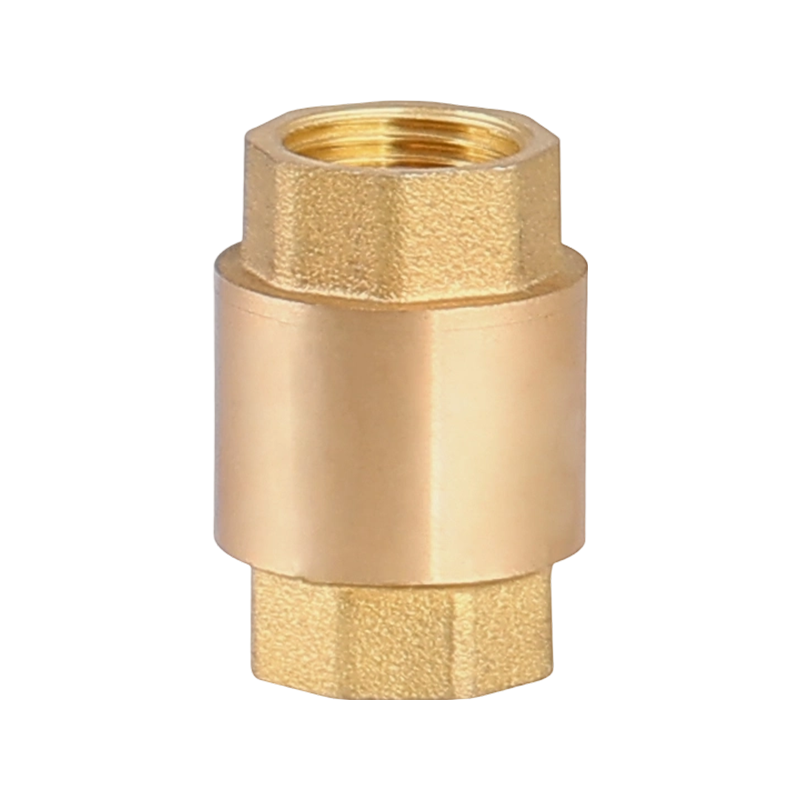
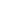A practical look at residential plumbing often raises questions about placement, especially when fixtures such as a Ball Valve Faucet and a PPR Ball Valve are u...
As a China Check Valve With Ball Valve suppliers and Aluminum Pipe And Fittings factory, we are mainly engaged in wholesale Tube Pipe Fittings, With advanced production equipment, strong technical force, outstanding quality, perfect after-sales service, and a good reputation, Pengbang has been rated as the promotion and application product by China's construction and decorative industry and won the top ten brands of China's valve manufacturing industry. The products sell in more than 50 countries and regions. such as the United States, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Australia, and are highly praised by many customers at home and abroad for "integrity, pragmatism, persistence, innovation" management concept; "excellence, continuous improvement, customer satisfaction quality policy; "people-oriented, unlimited service" business purpose is pengbang people's unswerving belief.
-
-
A closer look at everyday plumbing fixtures often begins with understanding how different flow structures behave, especially when products such as a Ball Valve ...
-
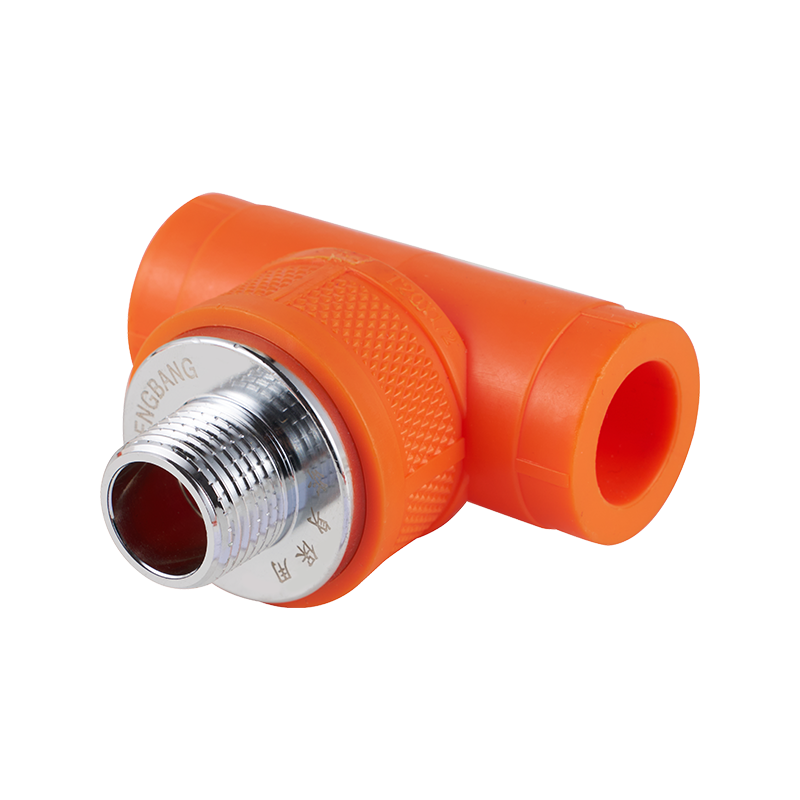
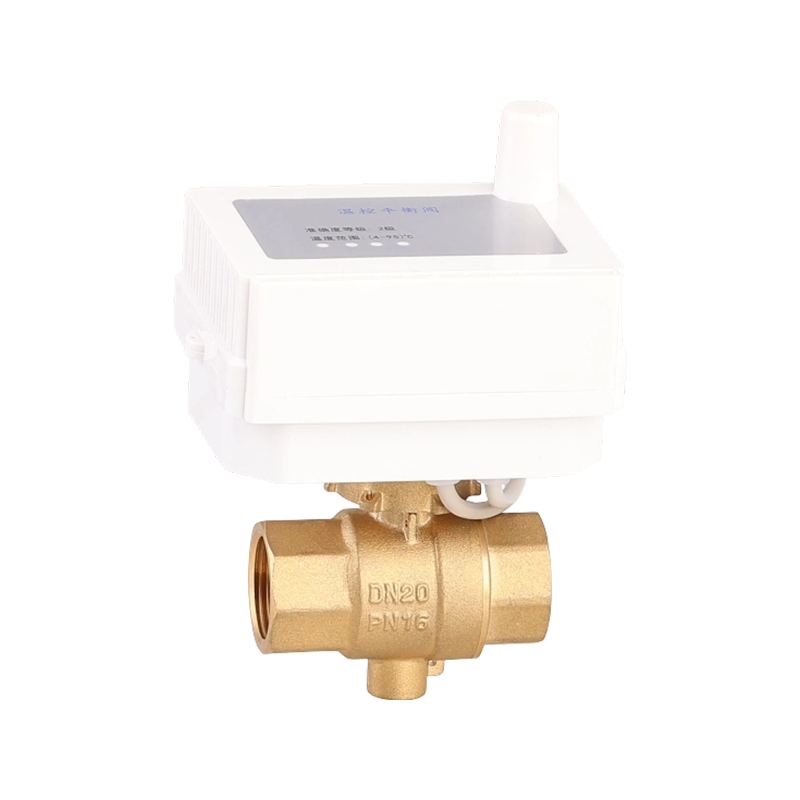
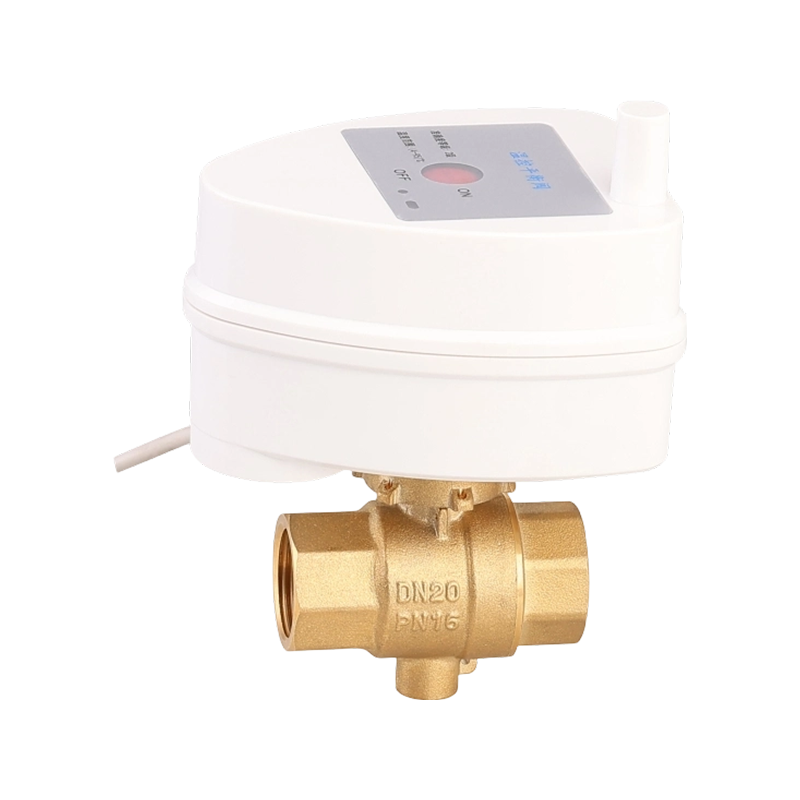
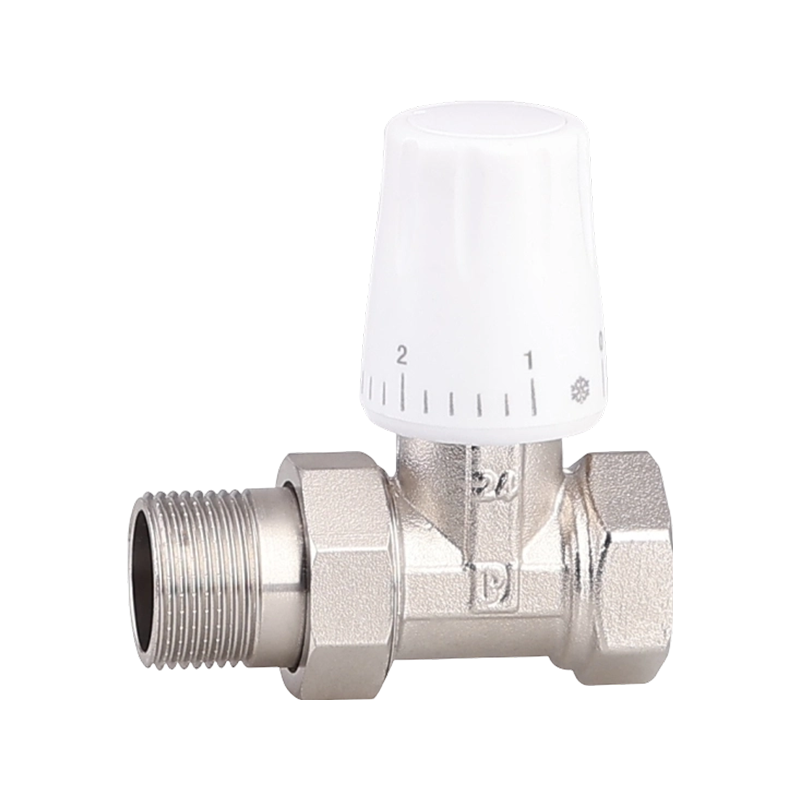
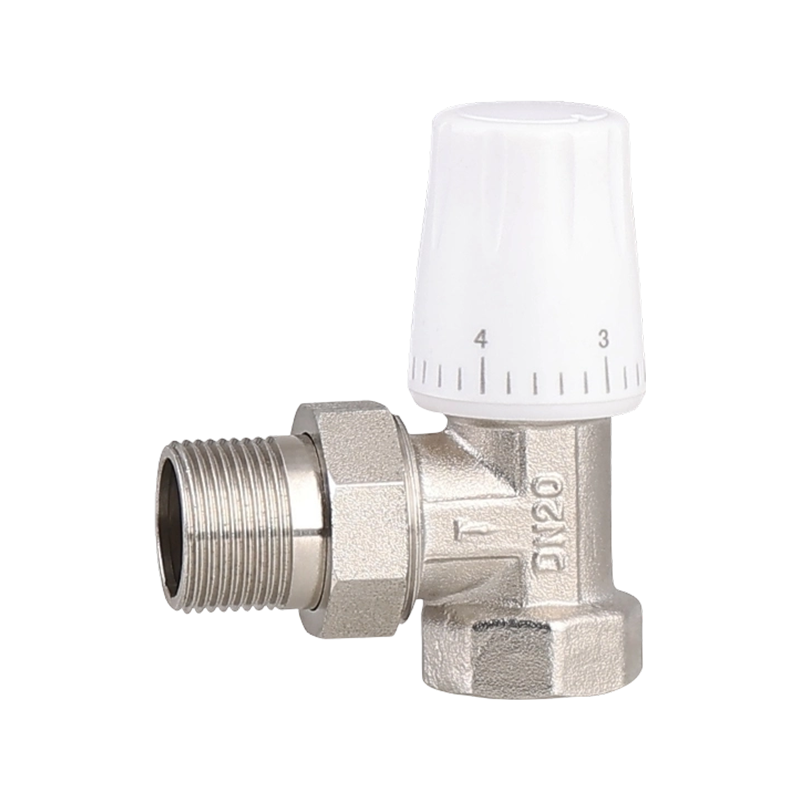
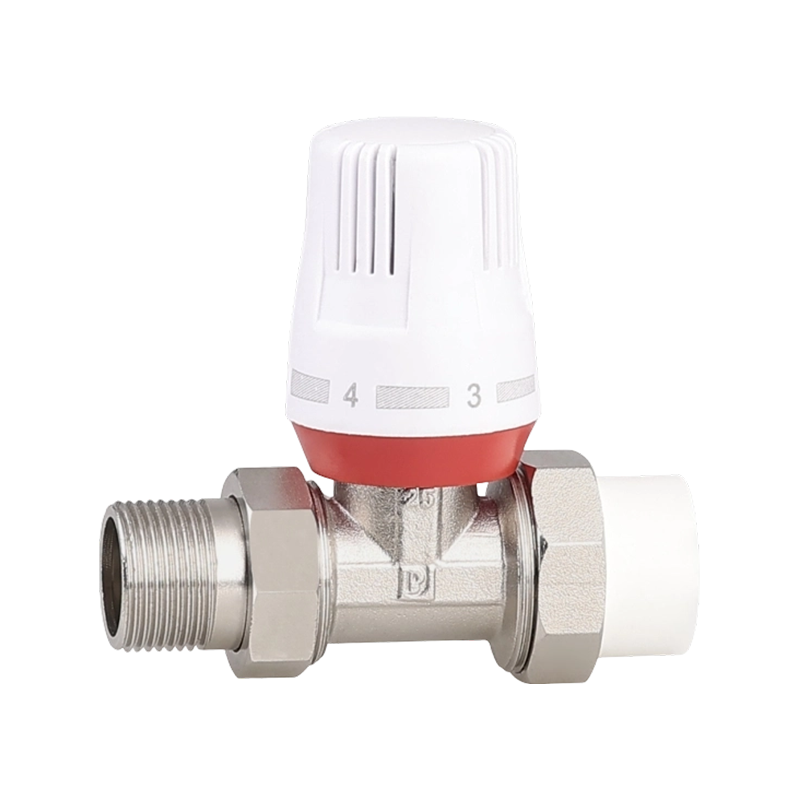
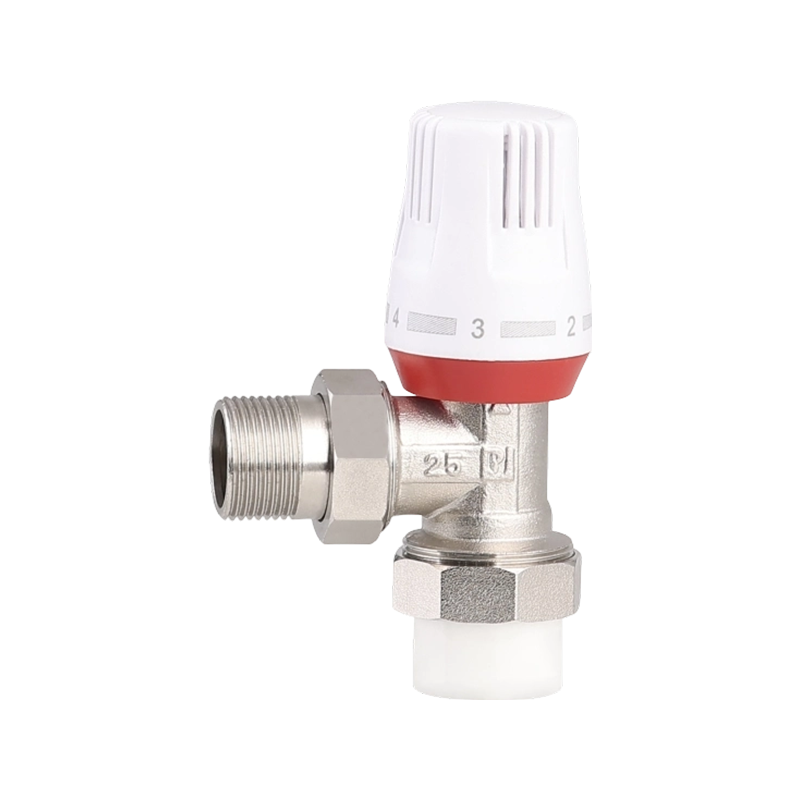
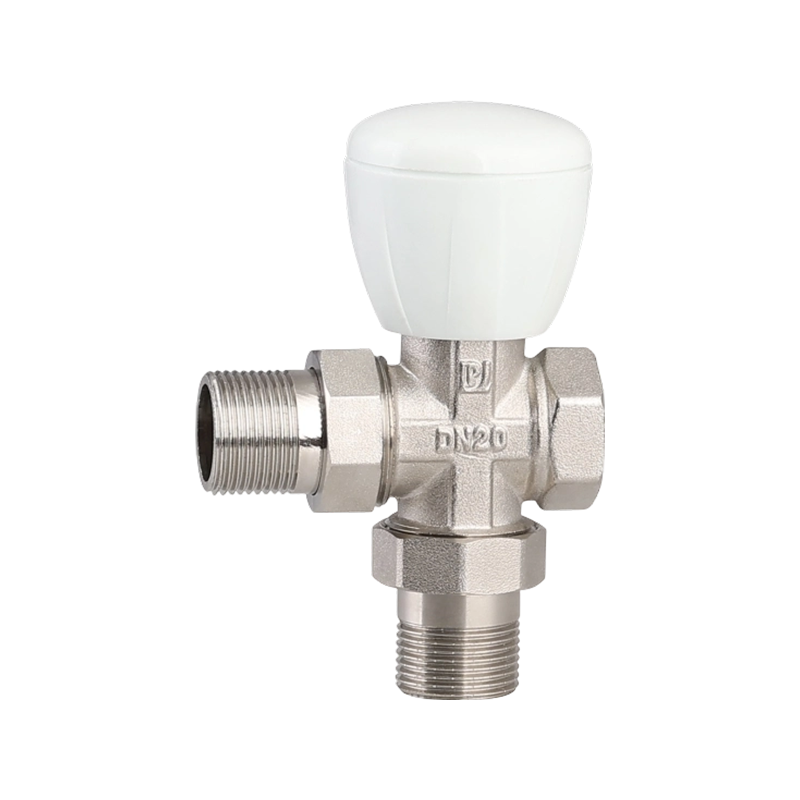
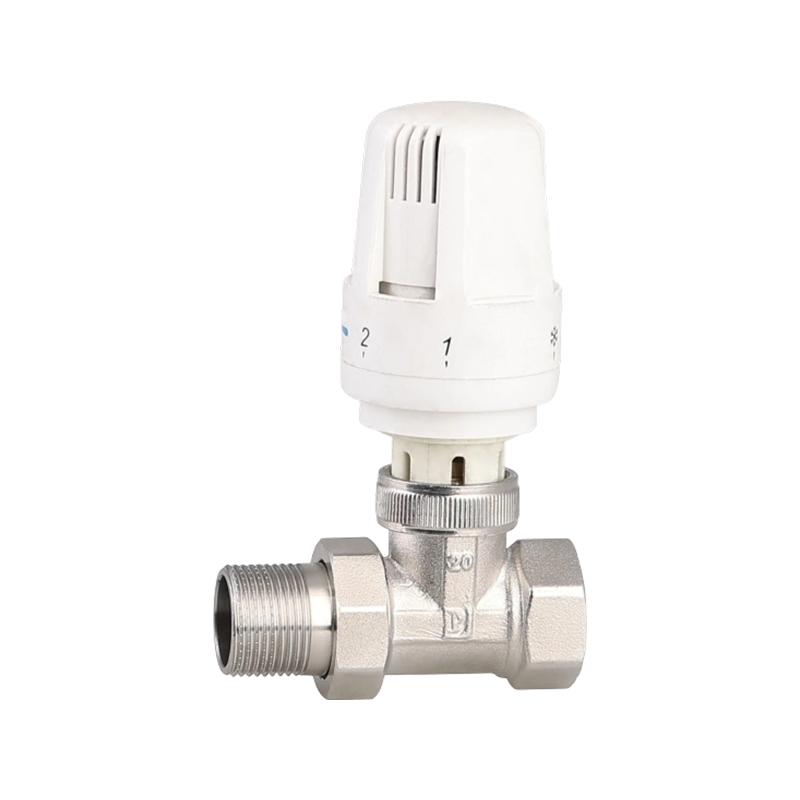
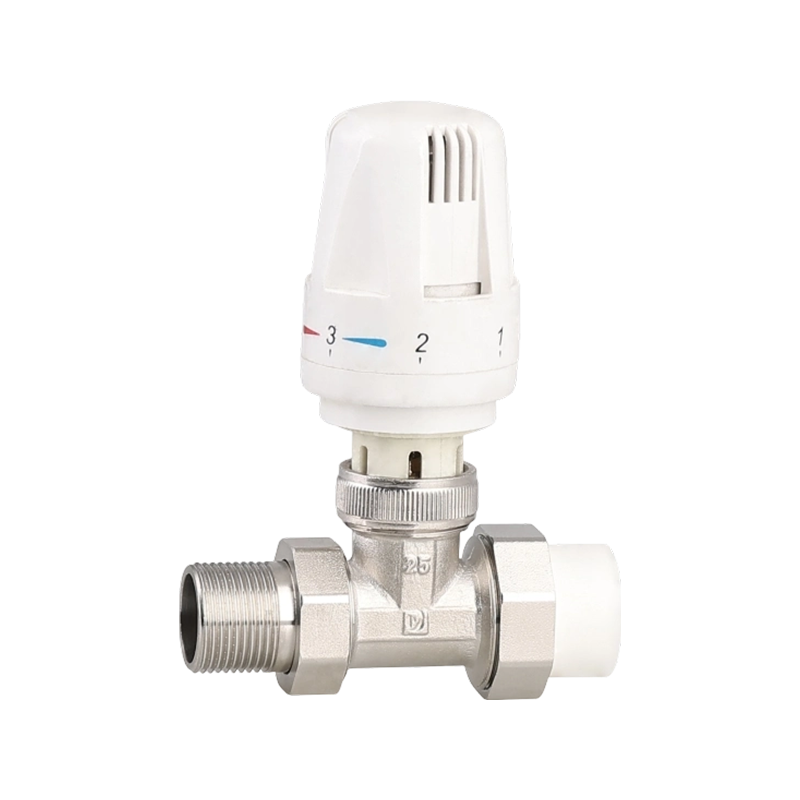
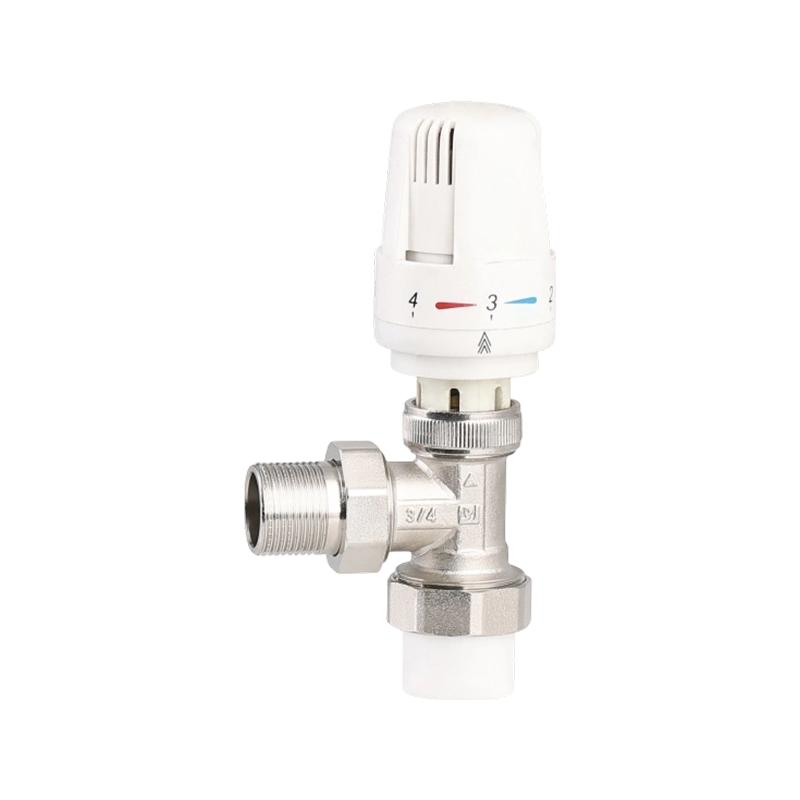
Efficient fluid handling and precise temperature regulation play an important role in meeting environmental standards in heating, cooling, and industrial system...
-
From October 23 to 27, we participated in the 138th Canton Fair, where the vibrant exhibition hall allowed us to showcase our valve fittings, heating pipe valve...
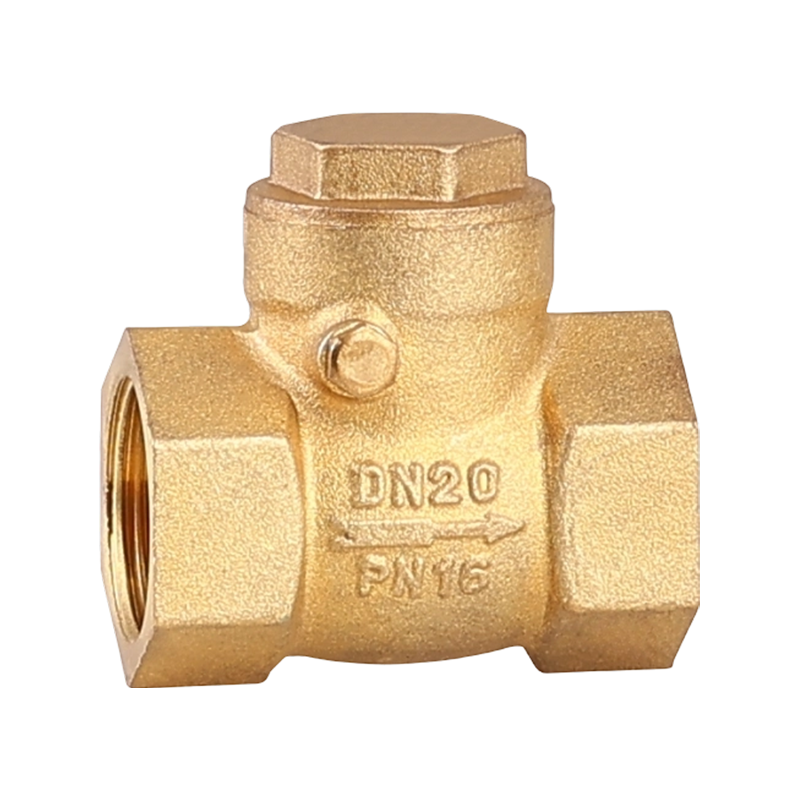
check valve with ball valve Industry Knowledge Extension
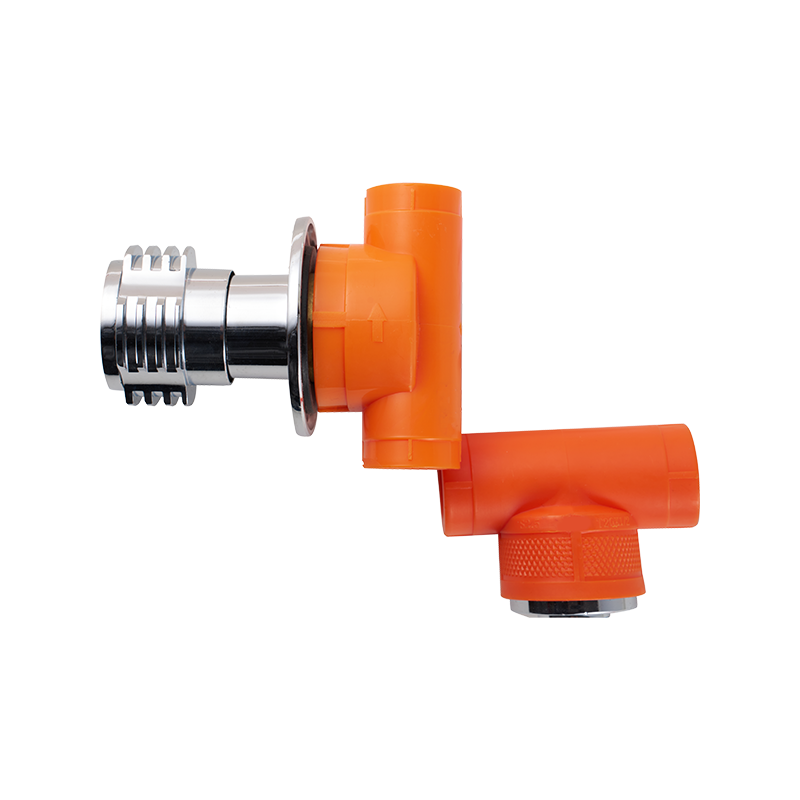
Check Valve with Ball Valve
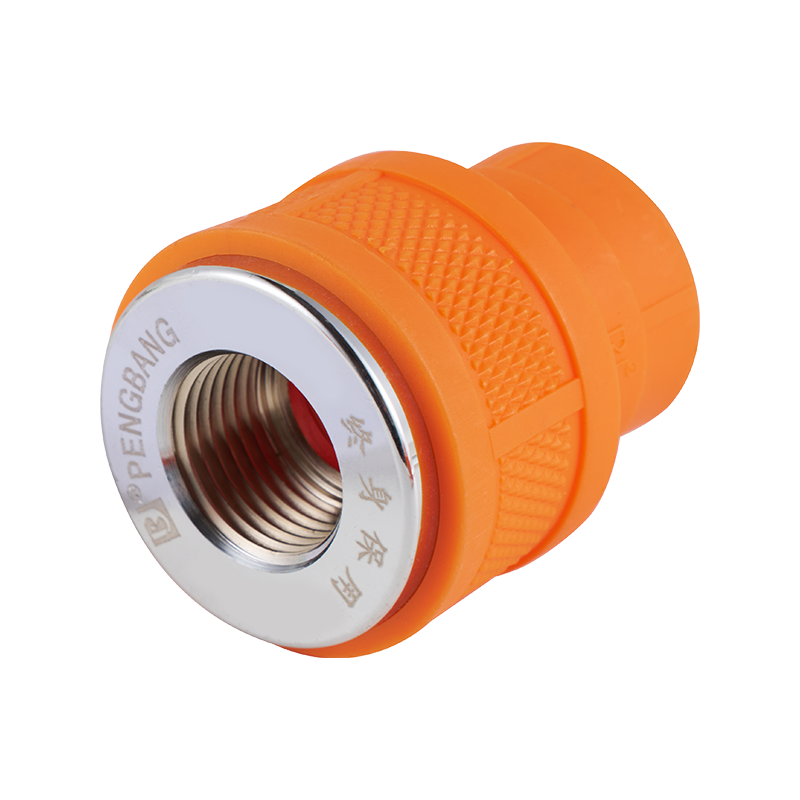
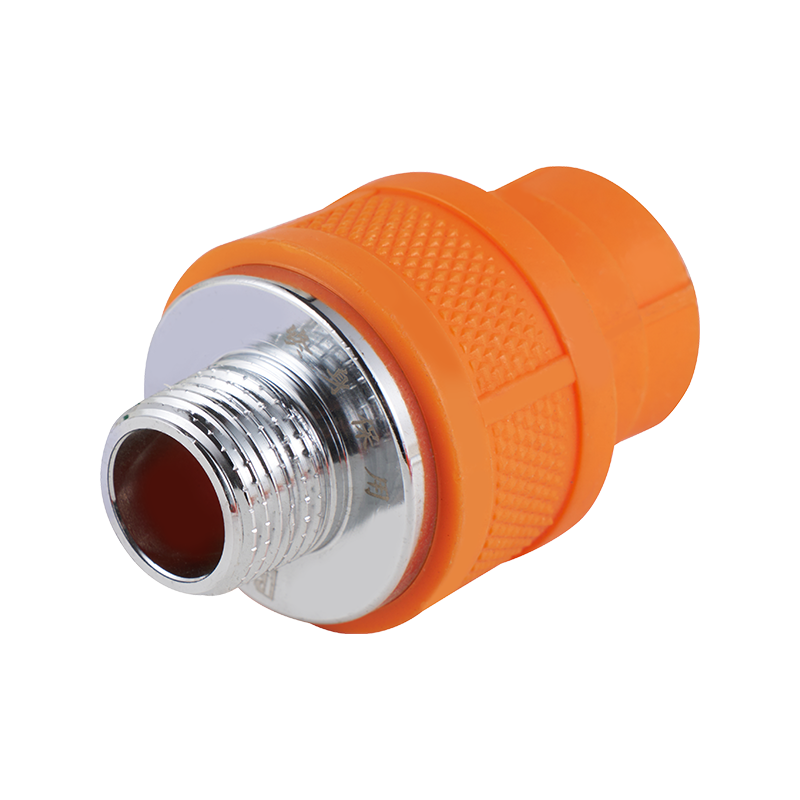
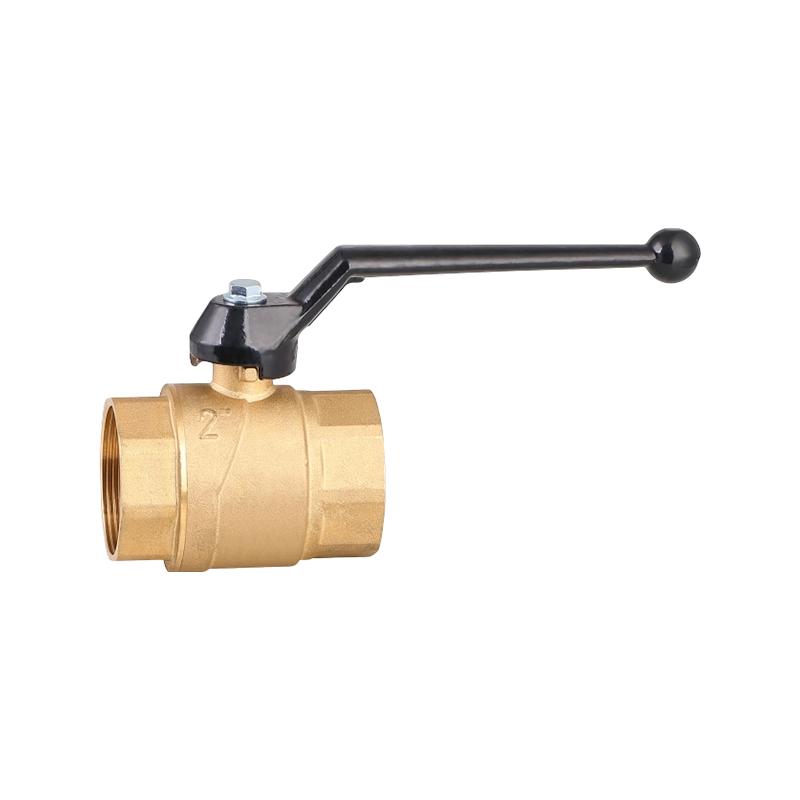
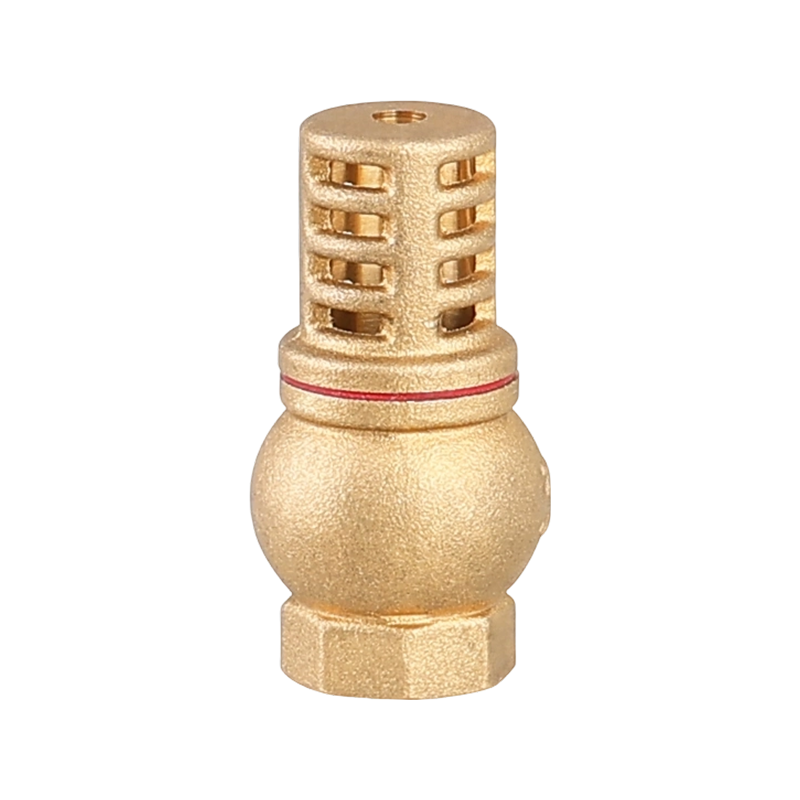
A check valve with ball valve combines two essential valve functions into one compact unit. The check valve allows fluid to flow in only one direction, preventing backflow that could damage equipment or disrupt system performance. The integrated ball valve provides manual control to start, stop, or regulate flow as needed. This combination is often used in piping systems where backflow prevention and easy isolation are necessary. The ball valve typically features a spherical closure element that rotates to open or close the flow path, offering reliable sealing and straightforward operation. The check valve part usually contains a spring-loaded ball or disc that automatically closes when flow reverses. Together, they help maintain system stability and protect pumps, compressors, and other sensitive components. Materials used in these valves vary depending on the application, ranging from brass and stainless steel to plastic composites, ensuring compatibility with different fluids and operating conditions. These valves are common in water supply, HVAC, and industrial fluid control systems, where maintaining unidirectional flow with the ability to shut off flow quickly is important. Installation is typically inline, and maintenance involves regular inspection to ensure the ball seats and seals remain intact. Overall, the check valve with ball valve is a practical choice when combining flow control and safety features in one device.
Aluminum Pipe and Fittings
Aluminum pipes and fittings are widely used in various industries due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. Aluminum offers a good strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it easier to handle and install compared to heavier metal pipes. The fittings are designed to connect aluminum pipes securely, ensuring leak-free joints and a stable pipeline system. These fittings come in various types, such as elbows, tees, couplings, and reducers, allowing flexible system design. The corrosion resistance of aluminum is a key advantage, especially in environments exposed to moisture or certain chemicals where steel pipes might degrade faster. Aluminum pipes also have good thermal conductivity, which makes them suitable for heat exchange applications or HVAC systems. Their non-magnetic properties can be important in specialized electrical or instrumentation systems. When choosing aluminum pipe and fittings, it is important to consider the specific alloy and temper to ensure the required mechanical properties and durability. Surface treatments like anodizing or coating can further improve corrosion resistance and appearance. Aluminum piping systems are common in construction, automotive, refrigeration, and industrial processes, providing a balance of durability and ease of use.
Tube Pipe Fittings
Tube pipe fittings serve as essential components in piping systems by connecting sections of tubing or pipes securely and efficiently. They come in a wide range of styles and sizes to accommodate different piping materials and system requirements. Common types include compression fittings, flare fittings, push-to-connect fittings, and threaded fittings, each offering distinct advantages depending on installation needs and fluid types. These fittings ensure a tight seal to prevent leaks and maintain system integrity under varying pressure and temperature conditions. The materials used for tube pipe fittings include stainless steel, brass, copper, and plastic, chosen based on factors like corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical compatibility. Proper selection and installation of fittings are critical to system performance, especially in industrial and mechanical applications where fluid control precision is necessary. Tube pipe fittings are often designed for ease of assembly and disassembly, which supports maintenance and system modifications without significant downtime. Their role extends across water supply, gas distribution, chemical processing, and pneumatic systems. Understanding the compatibility between tubing and fitting materials, along with the operating environment, helps ensure reliable and long-lasting connections in piping infrastructure.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى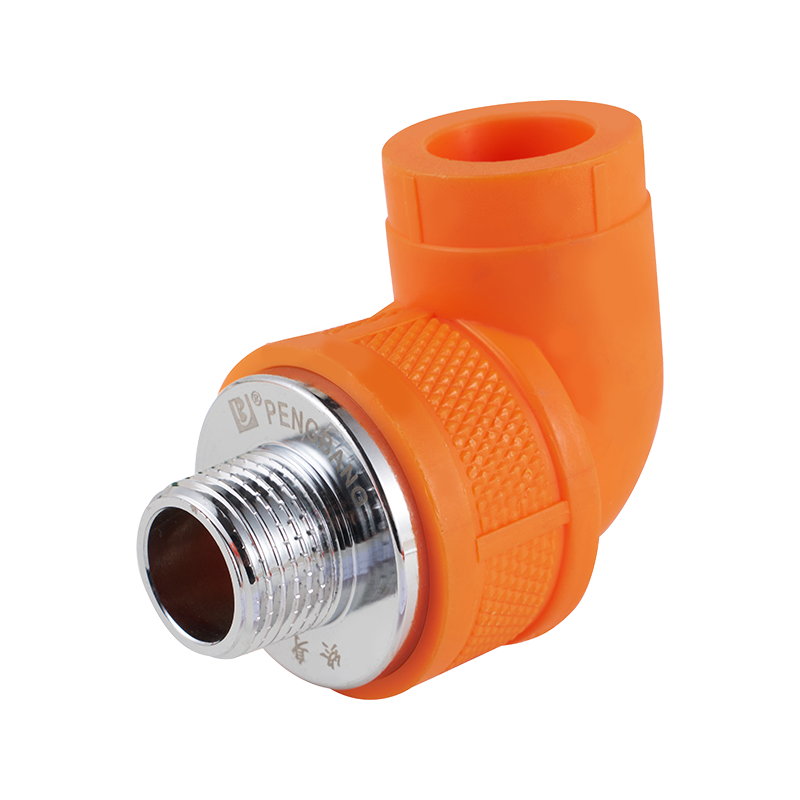



































 CONTACT US
CONTACT US